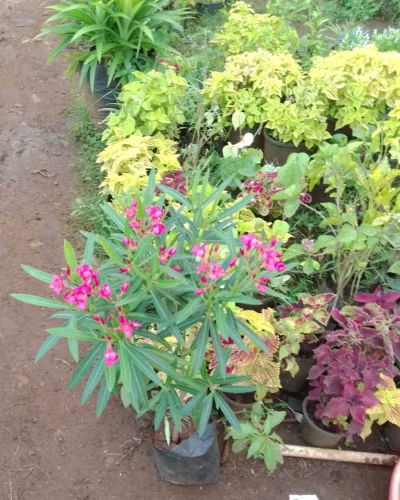
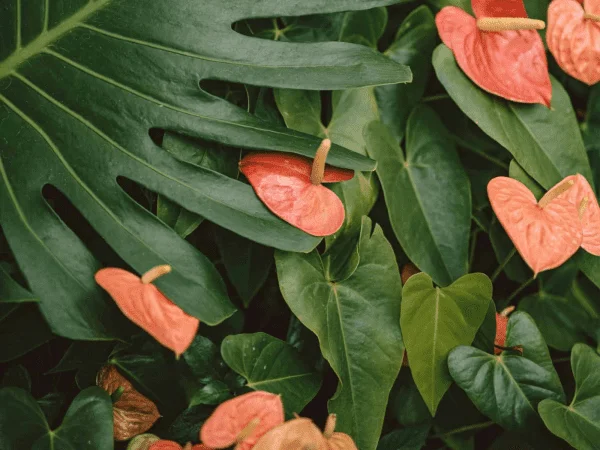
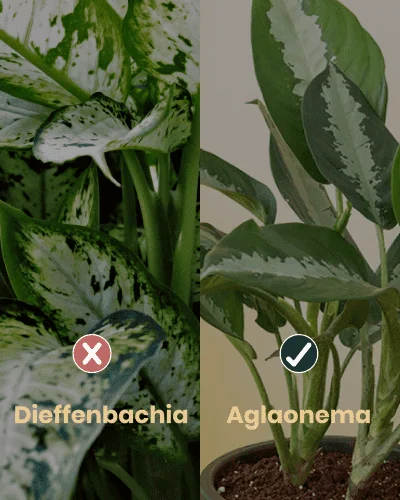
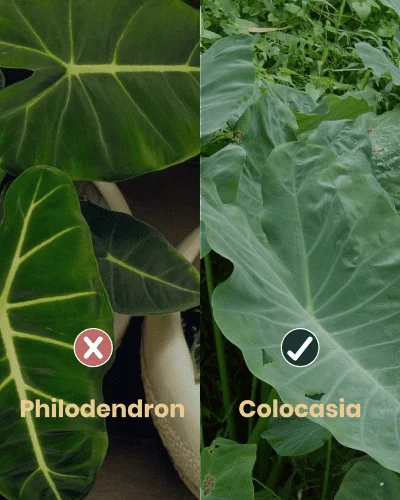
Winters in Mumbai may not be as harsh as the northern cities. However, they could be the same for plants. The cold weather brings its own set of challenges for plants. With pest attacks such as the powdery mildew, mealy bugs, white flies, etc, plants are more prone to diseases and decay in winters than any other season.
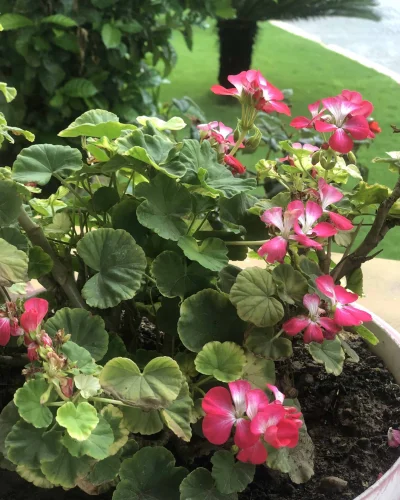
Hence, while adding plants to your garden, choose a mix of both evergreen and seasonal flowers. This way you can keep your garden colourful and lively at all times.
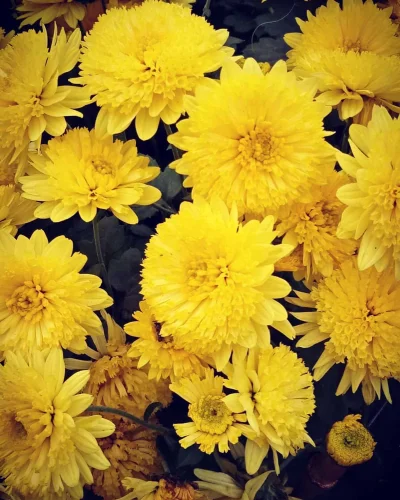
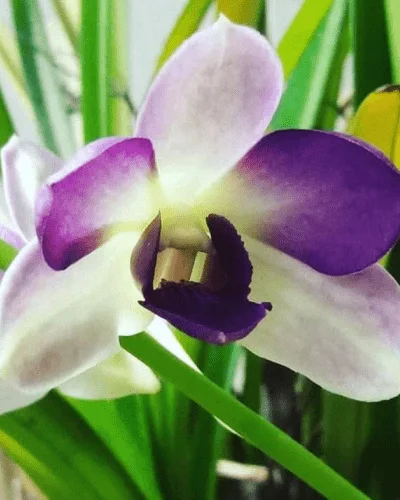
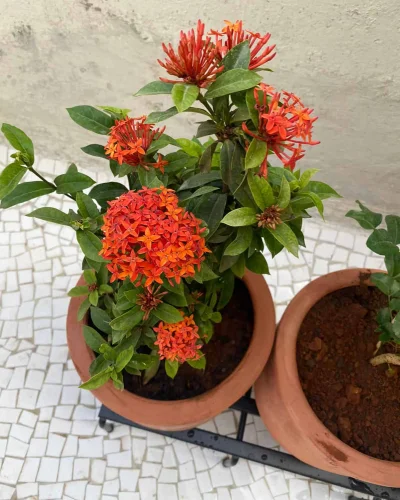
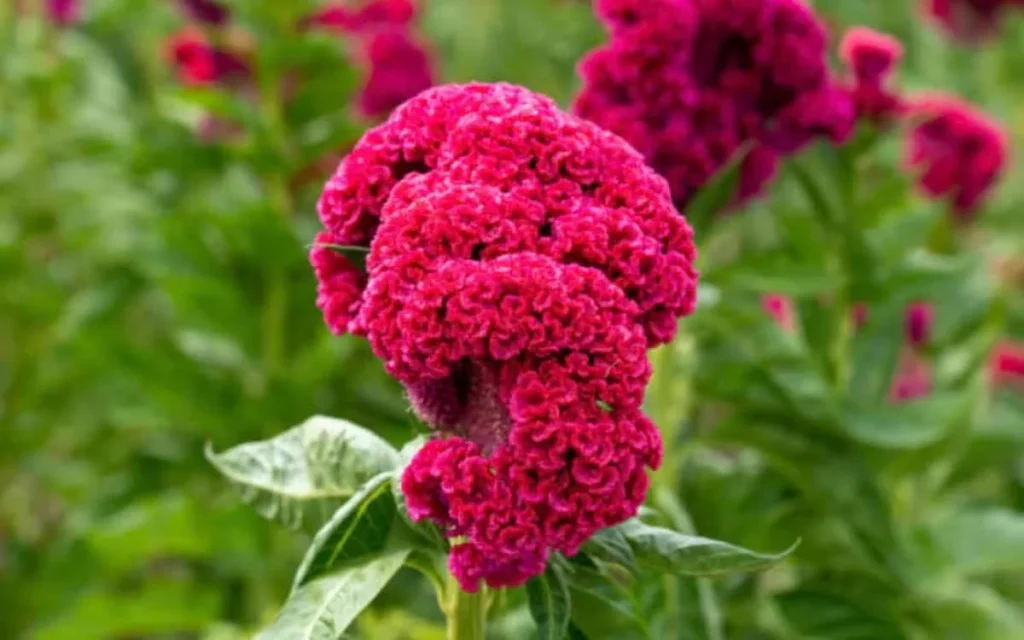
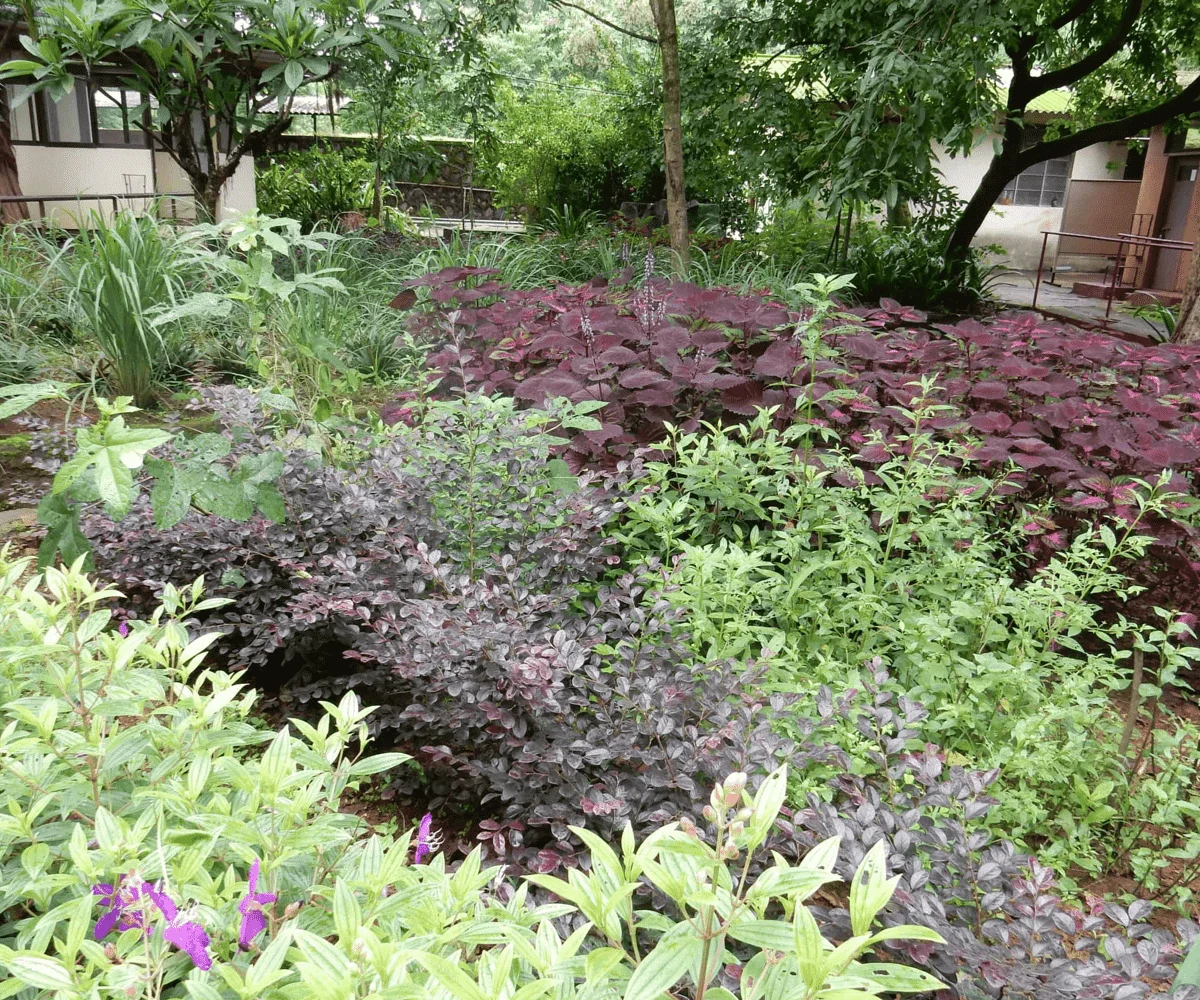
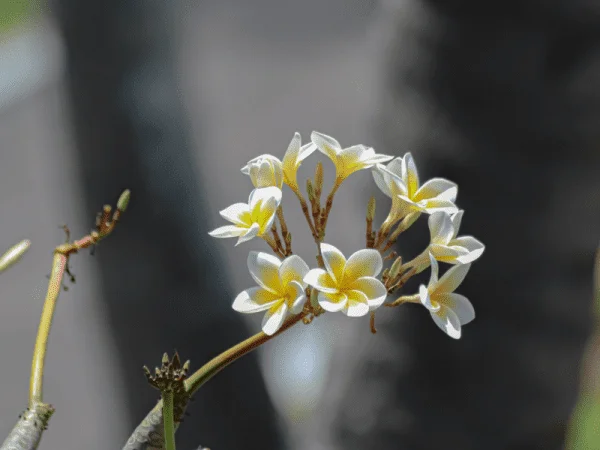
When it comes to perennial flowering plants, you can opt for Orchids, Kaner, Ixora, Roses. On the other hand, winter blooming flowers such as Sevanti or Chrysanthemums, Kalanchoe, Begonia, Hydrangeas can add vigour to your garden.
These native flowers are not just hardy in nature but beautiful in blooms and foliage. So go on and bring them home now!
Hence, while adding plants to your garden, choose a mix of both evergreen and seasonal flowers. This way you can keep your garden colourful and lively at all times.
When it comes to perennial flowering plants, you can opt for Orchids, Kaner, Ixora, Roses. On the other hand, winter blooming flowers such as Sevanti or Chrysanthemums, Kalanchoe, Begonia, Hydrangeas can add vigour to your garden.
These native flowers are not just hardy in nature but beautiful in blooms and foliage. So go on and bring them home now!